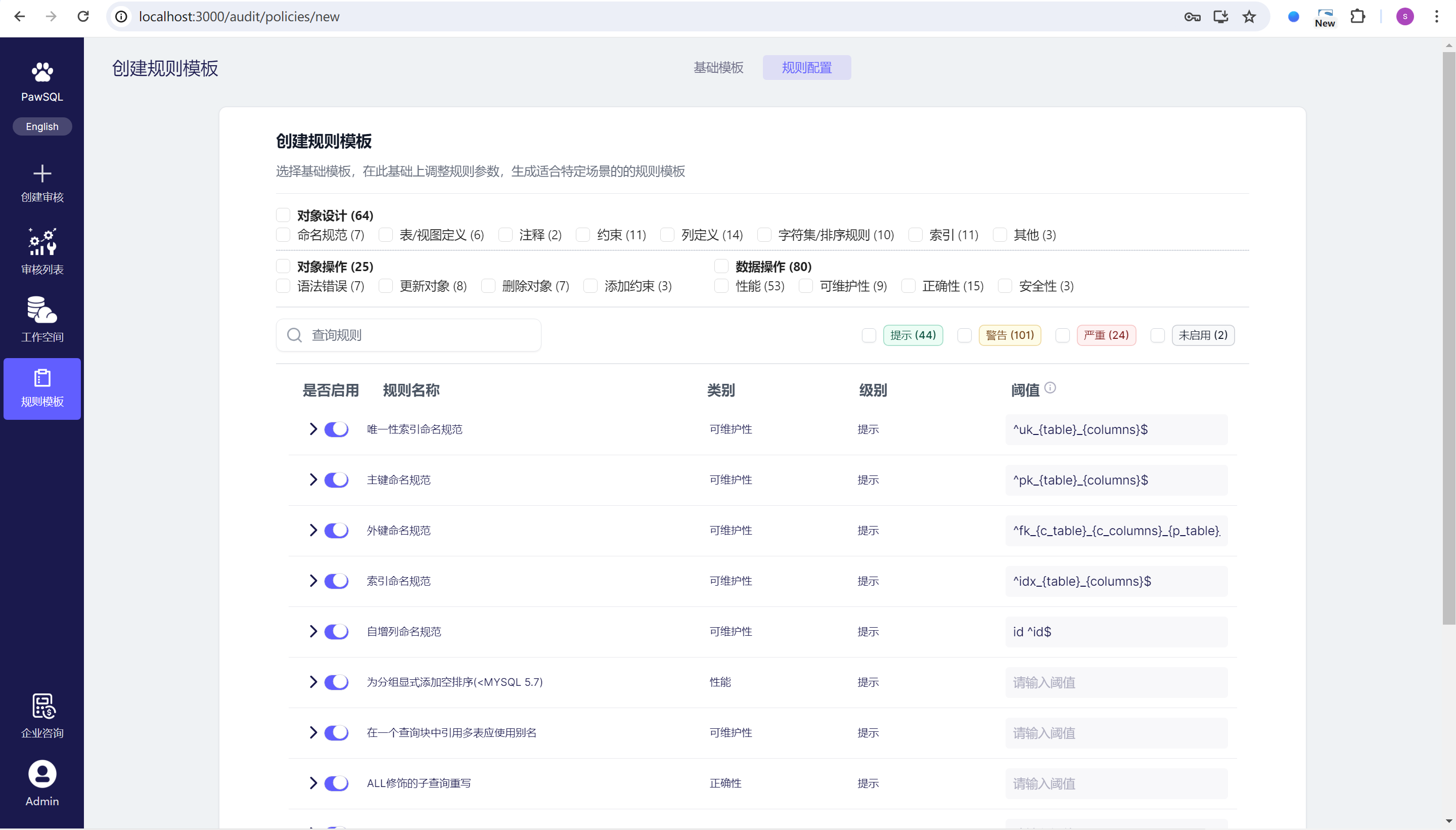
2. Customize Audit Policy
An SQL audit rule Policy refers to a set of predefined rules used to check the compliance, performance, and security of SQL statements during the SQL audit process. These Policys include a series of check items, each defining specific audit standards or best practices. SQL audit tools typically use these Policys to automatically scan SQL code to ensure it follows established rules and guidelines.
Types of Audit Policys
- Global Policy
The global Policy is visible to all users. It is a pre-set audit Policy when the audit platform is installed, usually including a Policy that contains all rules, and a global Policy for each database type.
| No. | Name | Number of Rules |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Default | 171 |
| 2 | Default MySQL Database Audit Policy | 167 |
| 3 | Default PostgreSQL Database Audit Policy | 166 |
| 4 | Default openGauss Database Audit Policy | 163 |
| 5 | Default Oracle Database Audit Policy | 163 |
| 6 | Default Kingbase Database Audit Policy | 162 |
- Local Policy
Local Policys are only visible to the user who created them or members of the team where the user who created them is located. Local Policys need to be created based on global Policys or Policys visible to users.
How to Create a Rule Policy
Step 1. Select the Audit Database Type
Different database types may apply different audit rules, especially some rules that are specific to particular databases. So, when defining an audit rule Policy, we first need to determine the database type.
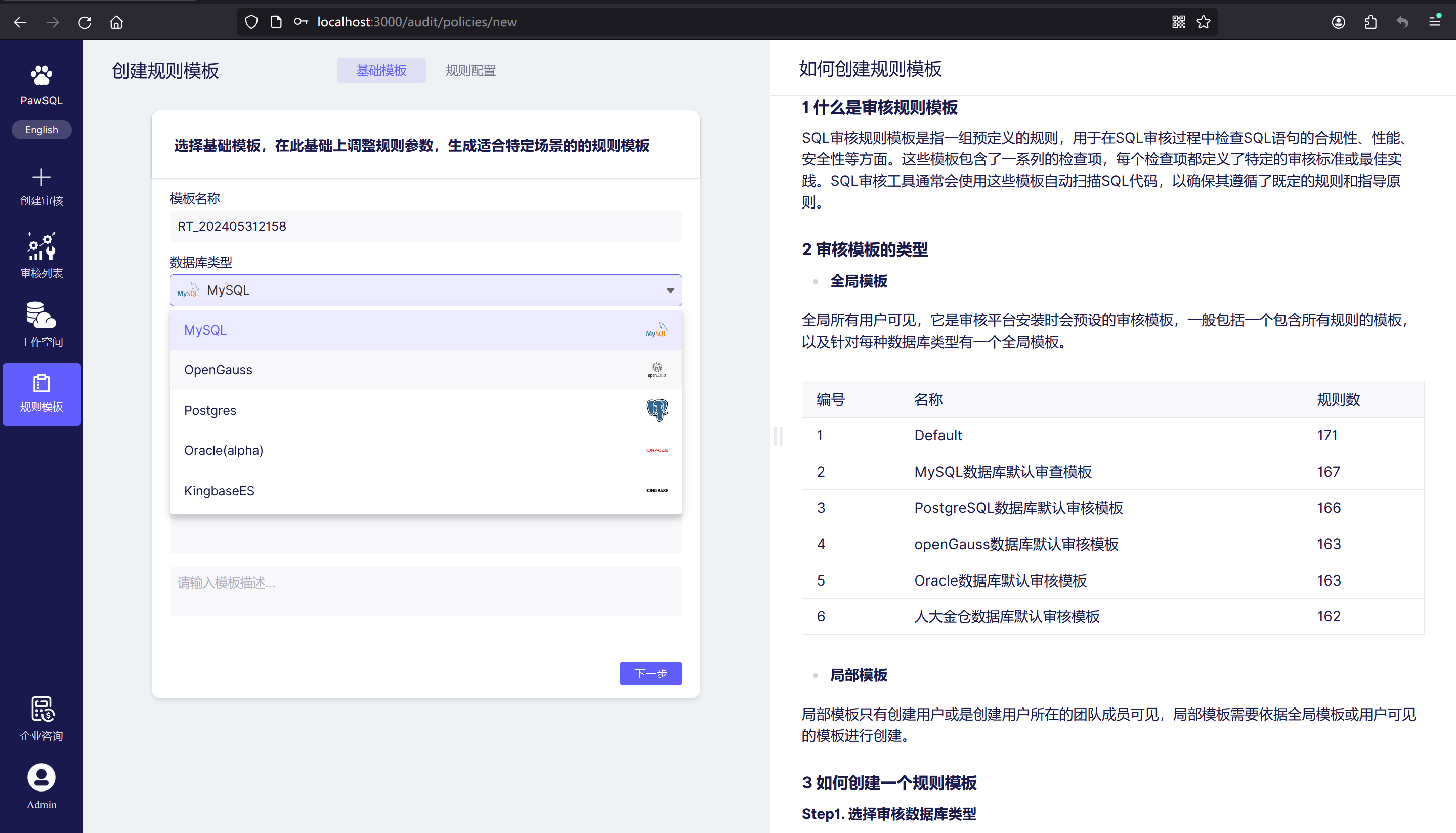
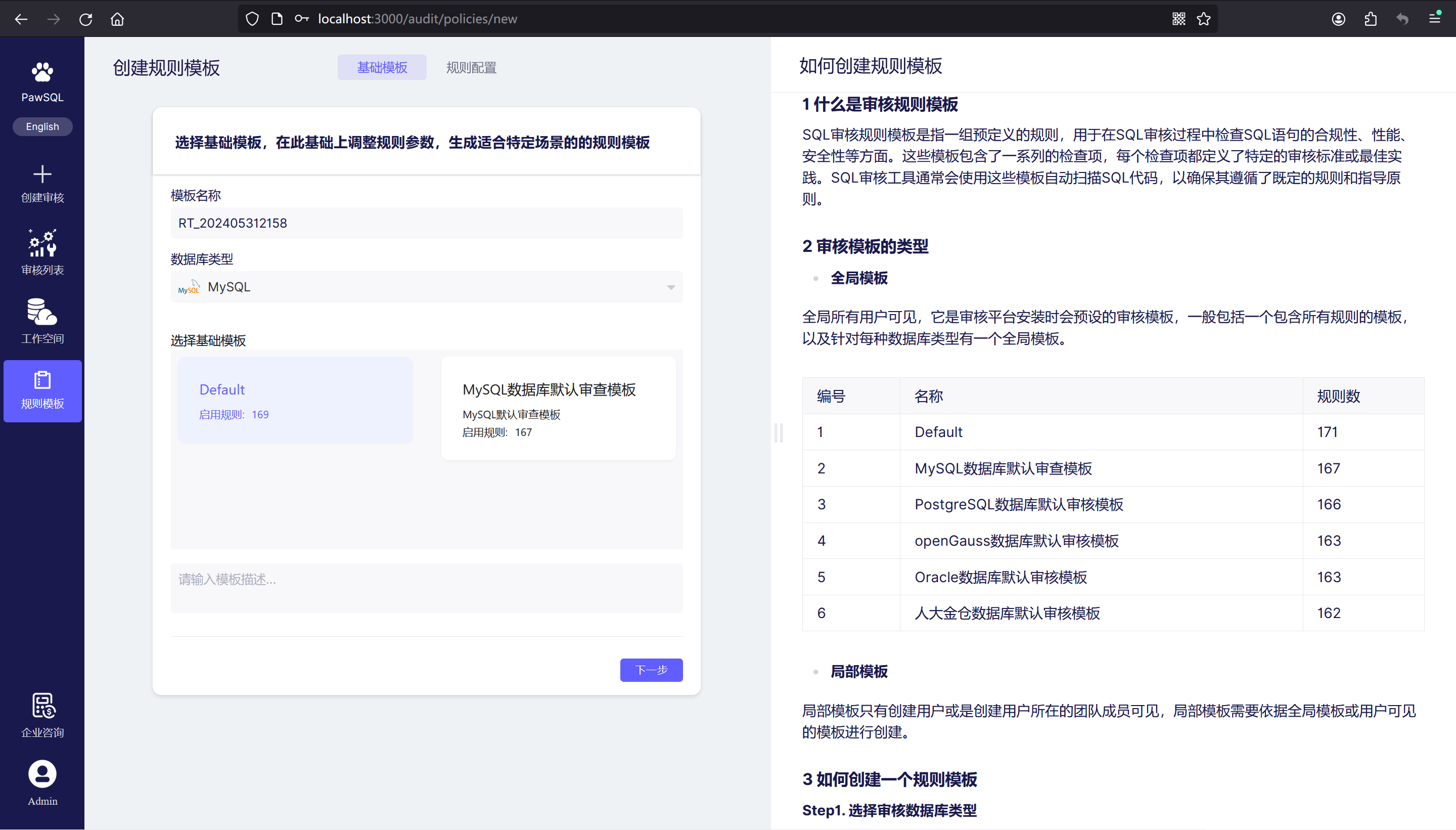
Step 2. Choose the Base Policy
The base Policy, from the perspective of database type, pre-enables effective audit rules and sets customized rule thresholds. By choosing a base Policy, you can quickly complete the settings for most rules; users can directly focus on the rules or thresholds they want to customize.
Step 3. Customize Rule Thresholds
Based on the settings of the base Policy, enable or disable specific rules and set the rule thresholds.