1. Create SQL Audit Task
SQL auditing, guided by SQL development standards, helps developers discover and fix potential quality defects, performance bottlenecks, and security risks in SQL statements through static code analysis, quality rule checks, and optimization suggestions. This improves the correctness, efficiency, readability, maintainability, and security of SQL code.
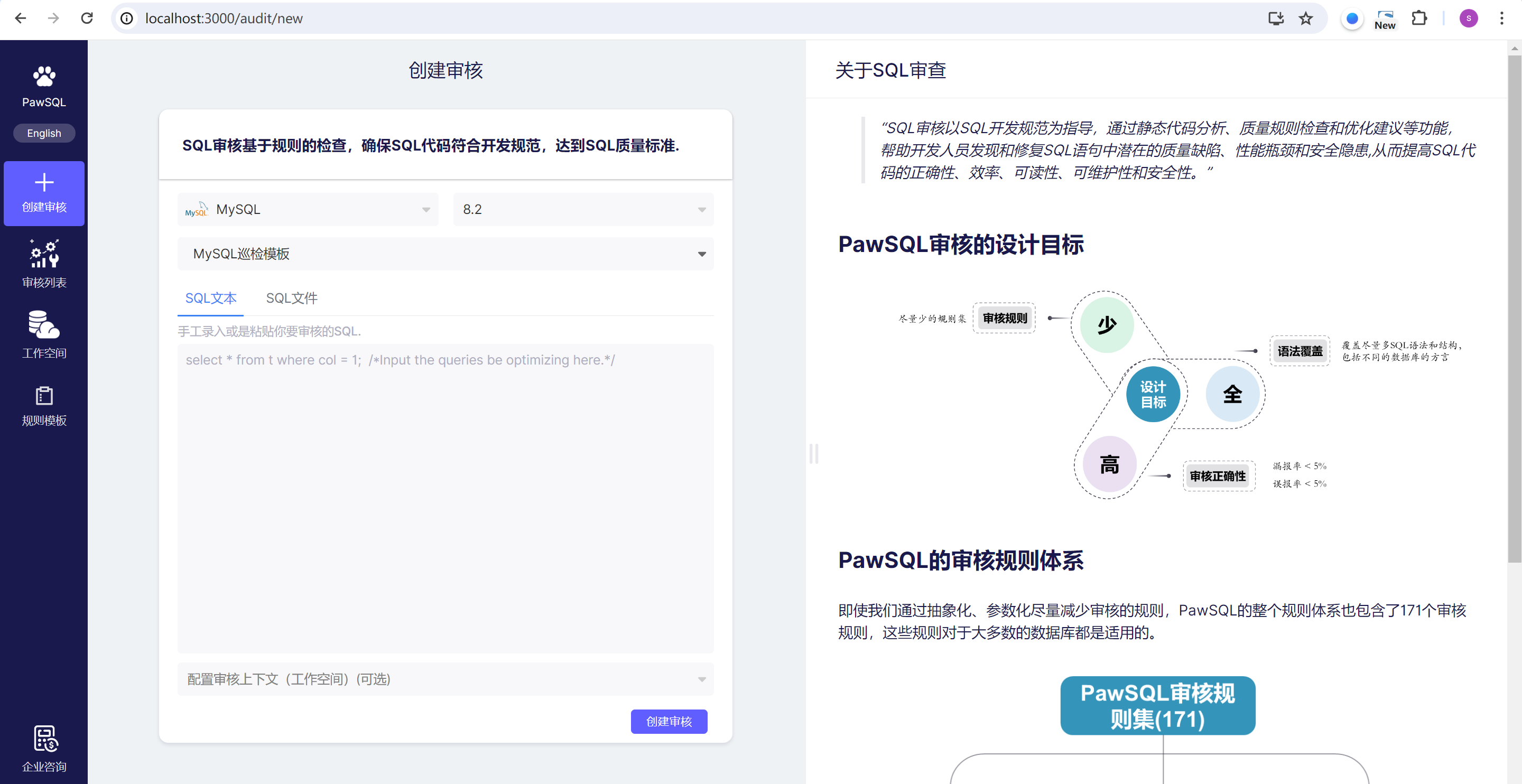
Step 1 Select Database Type and Version
- Different database types have different rule sets for review. Some rules are specific to certain database types, for example,
recommend using the INNODB storage engineonly applies to MySQL and its derivatives. - The same rule may require different parameters for different databases. For example, the
prohibited data typesrule, if you want to prohibit the use of floating-point data types, the parameters to fill in MySQL would befloat;double, while in PostgreSQL you might need to fill infloat;double;float4;double8. - Some rules may be related to specific database versions. For example, the rule
explicitly add null sorting for grouping (<MYSQL 5.7), if the MySQL database version specified by the user is greater than 5.7, this rule will not be triggered, even if the SQL contains matching SQL fragments.
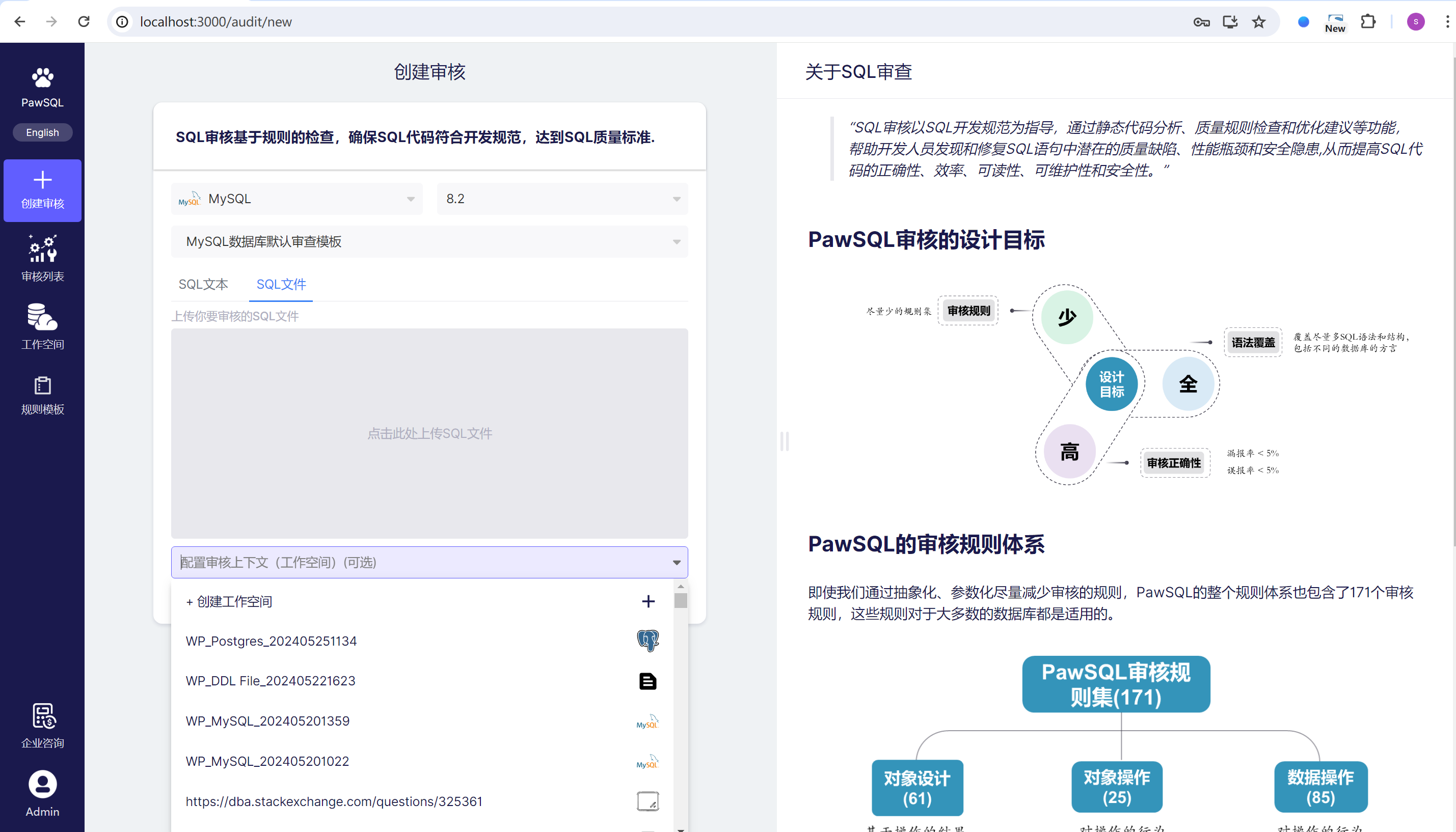
Step 2 Select or Create an Audit Template
After selecting the database type, PawSQL will automatically select the latest audit template that matches that database type; you can:
- Choose another audit template from the drop-down box;
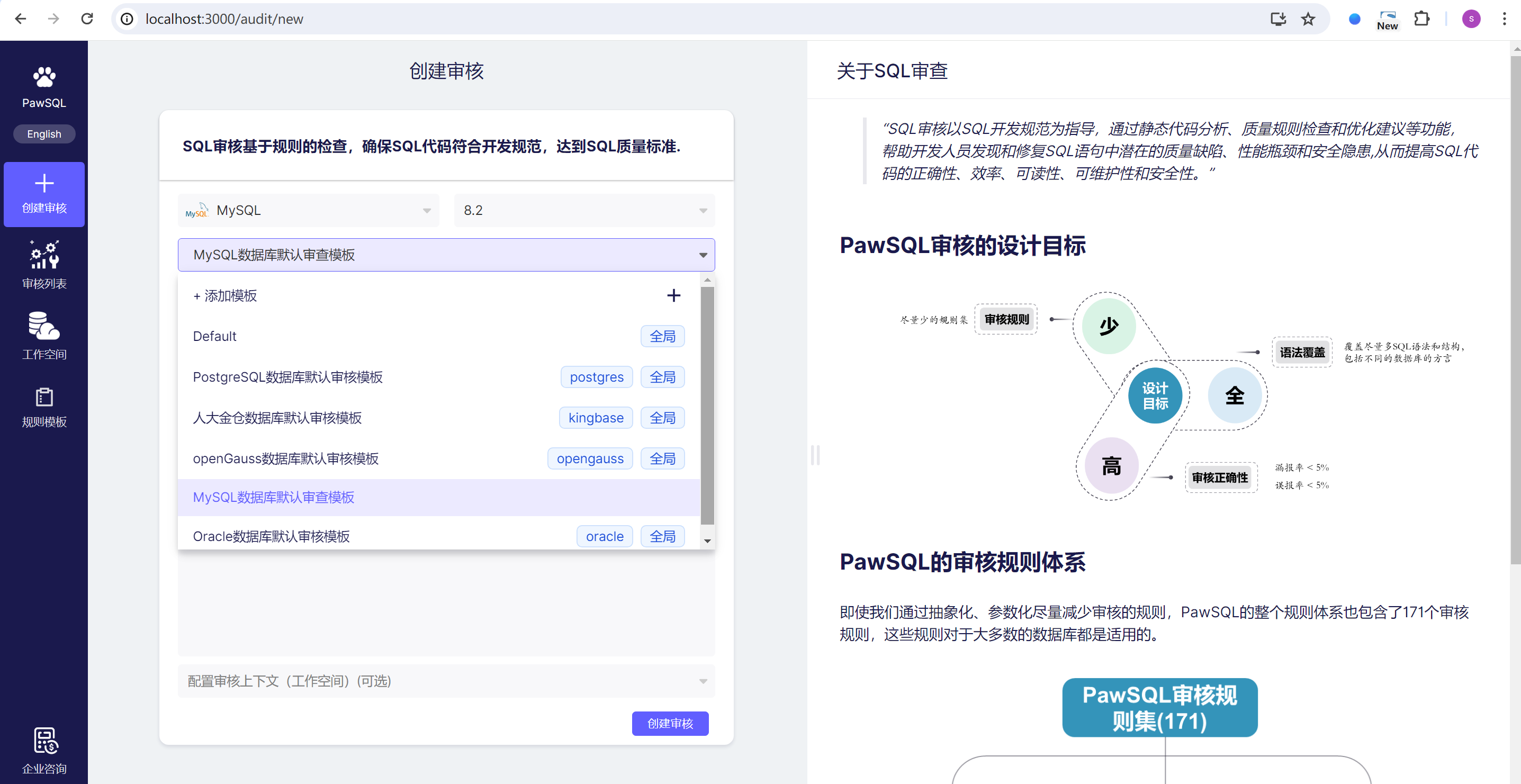
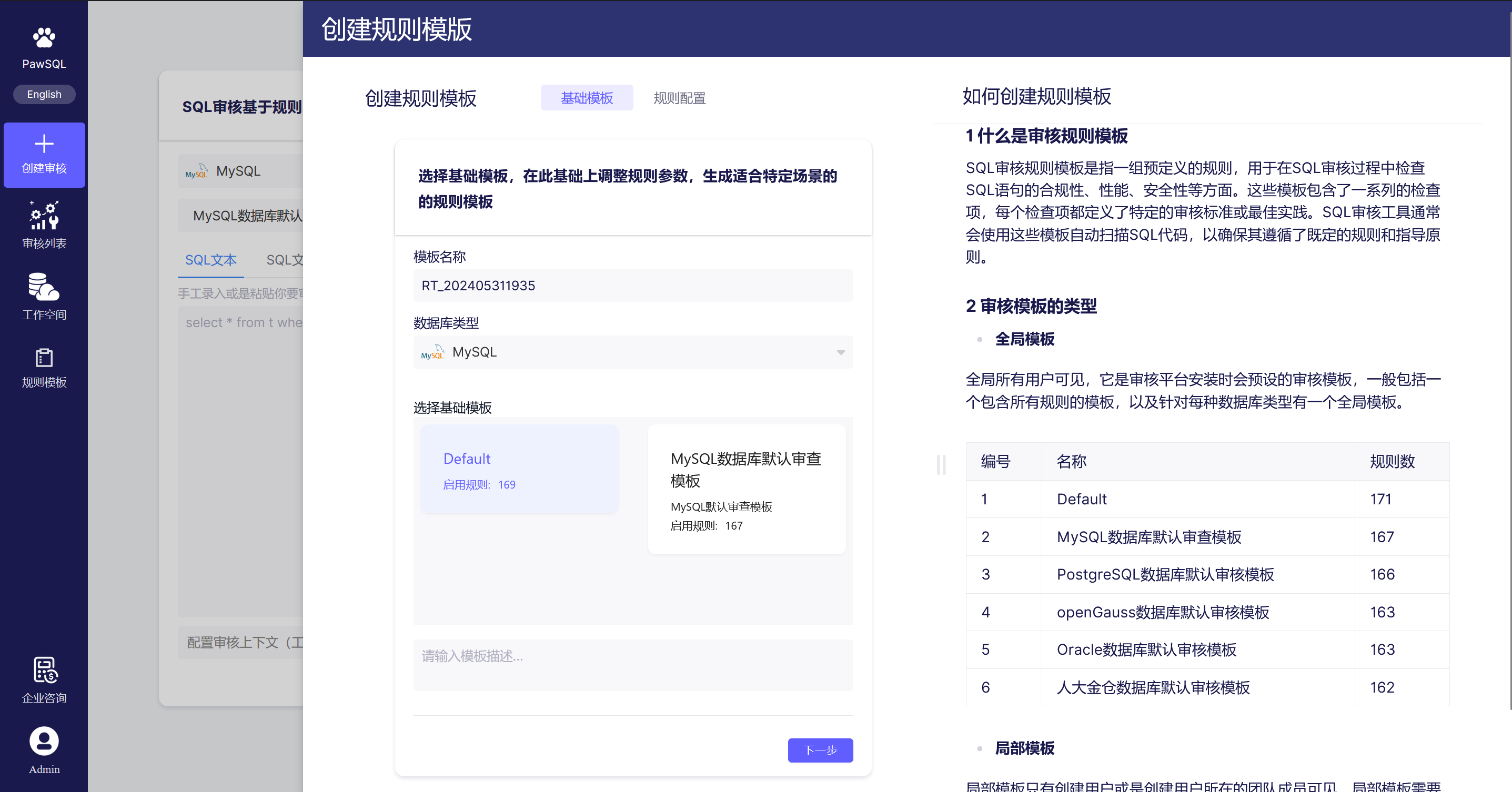
- Or add a new template through the add template option
Step 3 Enter the SQL Statements for Audit
Supports two ways of entering SQL statements,
- Enter SQL text, if there are multiple SQL statements, separate them with
; - Upload SQL files, if there are multiple SQL statements in the file, separate them with
;
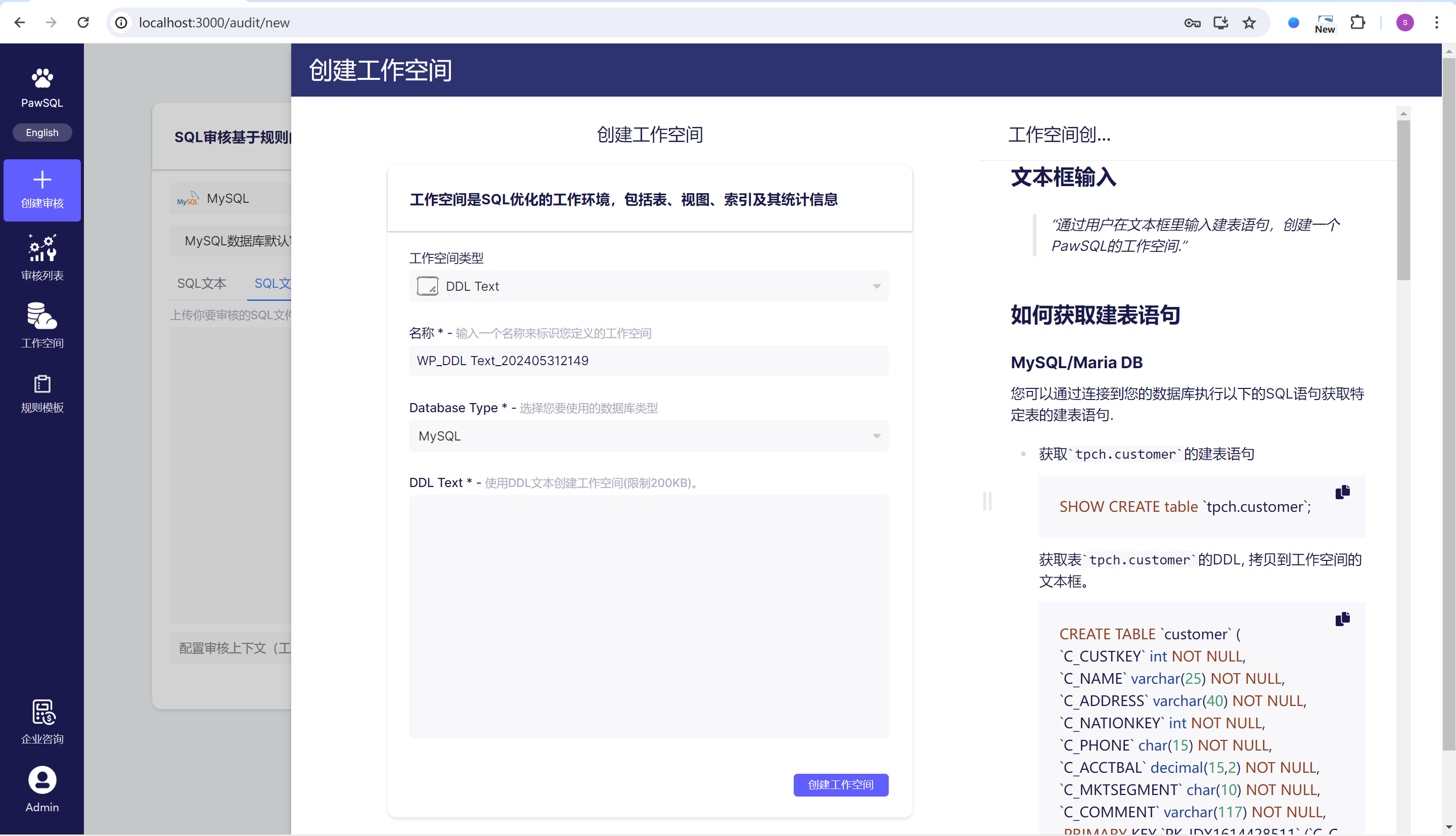
Step 4 Configure the Workspace (Optional)
The workspace is the context environment for SQL auditing in PawSQL, which generally includes the definitions of data tables, views, indexes, and some statistical information on them. It is not mandatory; an SQL audit task can be carried out in an existing workspace or without specifying a workspace.
- Select an existing workspace
- Create a new workspace