Outer to Inner Join Conversion
Copyright © 2024 PawSQL
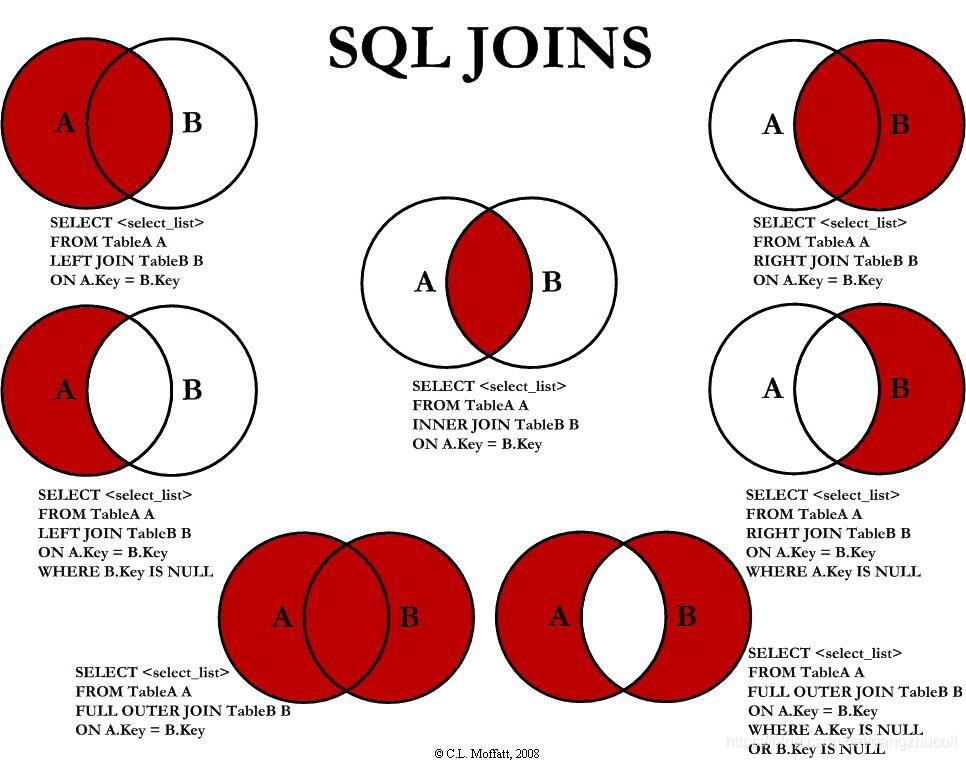
Types of Joins
The types of SQL joins mainly include inner join, outer join (left outer join, right outer join, full outer join), and cross join. C.L. Moffatt explains them very nicely in his article Visual Representation of SQL Joins in a visual way. You will find the information you need in following diagram he presented in his article.